Cyberattack statistics 2025
Discover these eye-opening cyber attack and cybersecurity trends and statistics and learn what they'll mean for your business in the next 12-24 months.
Index
- Costs of cybercrime
- Cybercrime for small and medium businesses
- Regions most affected by cyberattacks
- Types of cyberattacks on the rise in 2025
- Impact and severity of cyberattacks
- Cyberattacks by industry
- Cybersecurity industry statistics
- Data breach discovery statistics
- Who’s behind data breaches?
- How to reduce the risk of cyberattacks
- Cyber security trends and predictions for 2025
Protect your business today
Tell us a little about your business and we’ll create a coverage package that fits your needs, with a price you can count on.
Get a QuoteCyberattacks have quickly become one of the most significant threats to modern businesses.
The threat of cybercrime has never been higher. Advancements in artificial intelligence, rapid digitalization, and rising global tensions have made businesses more vulnerable. The cybersecurity industry is constantly adapting, and keeping up with the latest cyberattack news and trends can be challenging.
How can you prepare your startup for data security in 2025 and beyond? In this guide, we dissect the most important cybersecurity statistics, facts, figures, and trends as they relate to your startup.
Costs of cybercrime
The biggest risk posed by cybersecurity threats is financial loss. In fact, stats and trends show that cybercrime is one of the most costly threats to businesses. Worldwide, cybercrime costs companies an estimated $8 trillion in 2023, a staggering number that is expected to rise to nearly $24 trillion by 2027.
Cybercrime costs are expected to reach trillions in the coming years. Therefore, businesses must take proactive measures to mitigate financial risks. Understanding your company’s Risk Profile is a crucial step in identifying vulnerabilities and strengthening your cybersecurity strategy. Check your Risk Profile.
Cybercrime represents the greatest transfer of economic wealth in history.
Cybercrime for small and medium businesses
It is easy to assume that cybercriminals mostly target massive, publicly traded companies. However, attacks on small and medium businesses (SMBs) are actually on the rise — and for certain types of cybercrime, smaller businesses are even more at risk.
A cyberattack can be devastating for small businesses, disrupting normal operations and damaging important IT assets or infrastructure. This type of damage can be impossible to recover from without the budget or resources to do so. Cybersecurity is expensive to maintain and many smaller companies simply cannot afford the expense.
Nearly half of attacks affect small businesses
As we mentioned earlier, small businesses are by no means safe from cyber threats. In fact, 46% of all cyber events worldwide affect businesses with fewer than 1,000 employees.
41% of small businesses experienced a cyber threat
In 2023, small businesses were hit hard by cyberattacks, with more than 40% reporting an attack.
Small businesses are more likely to be targeted by phishing attempts
Companies with fewer than 100 employees receive 350% more social engineering attacks, such as phishing, than larger enterprises.
Many SMBs are not prepared for a cyber threat
Around half of all small businesses don’t have a cybersecurity plan. Additionally, around 33% of small businesses use free cybersecurity rather than professional-level solutions.
Regions most affected by cyberattacks
Some countries are better prepared for cyberattacks than others. And while most countries around the world are rapidly improving their systems, many are behind the curve. Here are a few regional statistics.
The United States accounts for 59% of all ransomware attacks
Ransomware is one of the most costly and disruptive cybersecurity threats. This type of cyberattack is on the rise in the United States, with 59% of all ransomware attacks taking place there.
Cyber incidents in other North American countries are on the rise
Attacks have also been increasing elsewhere in North America. In 2024, 72% of Canadian small to medium-sized businesses experienced a cyber attack. Meanwhile, 65% of Mexican businesses reported an increase in breaches.
Russia has the highest cybercrime threat level in the world
According to the World Cybercrime Index, Russia is by far the country most at risk of cybercrimes. There are several reasons for this, including organized criminal activity, Russian government involvement, and lack of legal enforcement.
Other at-risk regions include Ukraine, North Korea, Nigeria, the U.S., China, Romania, Brazil, and India.
In 2024, Poland had experienced the most cyberattacks in the world
Russia may have the highest risk, but Poland has been experiencing the most attacks. According to the country’s Cyberspace Defense Forces, Poland received over 1,000 cyberattacks per week in 2024. The country has seen a sharp uptick in cyberattacks since the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, and the Polish government has accused the Kremlin of many of the attacks.
Nordic countries have the best cybersecurity infrastructure
Finland, Norway, and Denmark have the strongest cybersecurity systems and are the most prepared for an attack.
Types of cyberattacks on the rise in 2025
Cyber threats are constantly evolving to bypass improved security systems and extort companies for more money and information. But what are the most common types of cyberattacks in 2025?
Malware
One of the most common cybersecurity risks, there are currently more than 1.2 billion malware programs in existence. Malware is an umbrella term for any kind of malicious software that can damage computer systems and assist cyber criminals. The number of detected malware programs slightly decreased in 2024, but the threat is by no means going away.
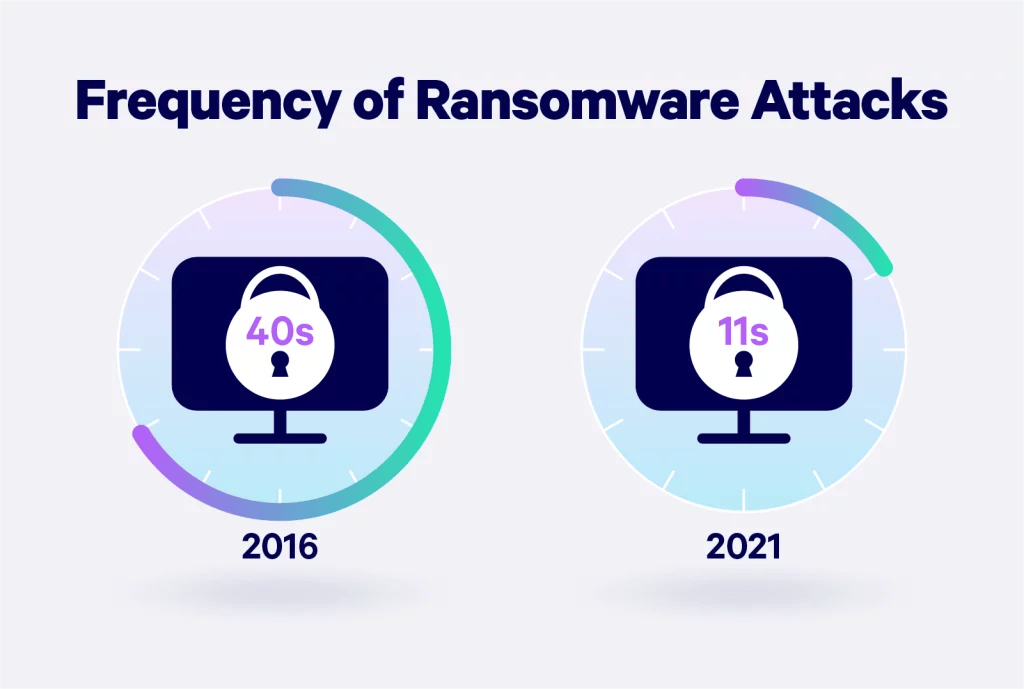
Ransomware
Ransomware is a specific type of malware that aims to force businesses to pay a sum to unlock files and data in their systems. This cyber threat is a form of extortion and is one of the most costly cyberattacks for businesses. Ransomware attacks have been on the upswing, growing by around 67% in 2023.
Social engineering is another common cyberattack affecting businesses. Cybercriminals manipulate employees by earning their trust to gain access to sensitive data.
The most frequent social engineering attack is phishing. Phishing perpetrators impersonate reputable companies and send messages to employees attempting to steal sensitive information, passwords, and bank details. According to Z Scaler, phishing attempts rose by 58.2% in 2023, and the finance industry was the most targeted sector.
Interestingly, around 43% of all recorded phishing attacks were imitating Microsoft.
Distributed denial of service attacks (DDoS)
Distributed denial-of-service attacks (DDoS) are a growing concern for businesses in 2025. A DDoS attack involves a criminal overwhelming a server by flooding it with traffic, potentially causing system downtime. This allows hackers to target vulnerabilities. In recent years, distributed denial-of-service attacks have escalated in frequency and sophistication. DDoS attacks increased by 13% in the first two quarters of 2024, with more than 8 million incidents.
Impact and severity of cyberattacks
Cyberattacks can impact an organization in many ways — from minor disruptions in operations to major financial losses. Regardless of the type of attack, every consequence has some form of cost, whether monetary or otherwise.
Consequences of the cybersecurity incident may still impact your business weeks, if not months, later. Below are five areas where your business may suffer.
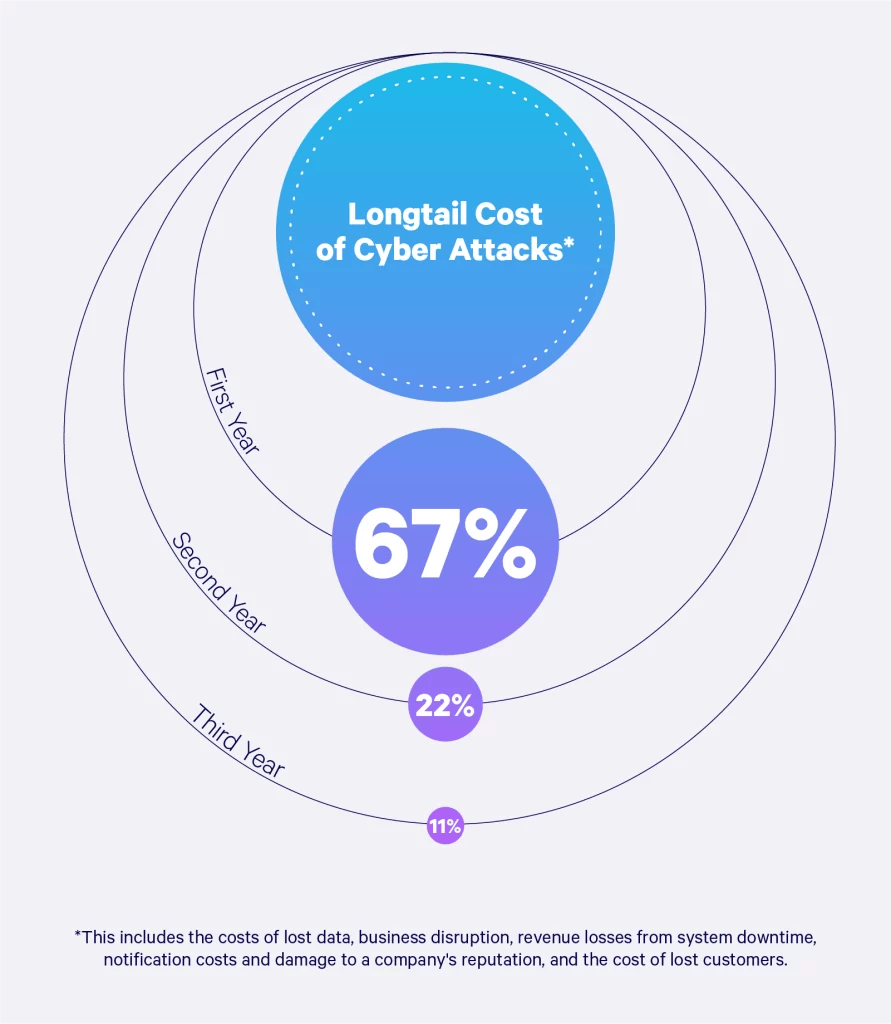
The long tail costs of a data breach can extend for months to years and include significant expenses that companies are not aware of or do not anticipate in their planning.
These costs include lost data, business disruption, revenue losses from system downtime, notification costs, or even damage to a brand’s reputation. In the visual below, we outline the impacts a business may face from the first year up to the third year.
Financial losses
According to the FBI International Crime Report, Americans lost $12.3 billion due to 2023 cyberattack incidents.
Cybercrime and data breaches are becoming more expensive. In 2024, the average cost of a data breach hit an all-time high of $4.88 million.
There are several ways a company could lose money during a cyber threat:
- Theft
- Regulatory fines
- Liability expenses
Loss of productivity
The most obvious impact of a cyberattack is financial losses, but a cyber threat can also disrupt your standard business operations, leading to a loss of productivity. Major malware or security breaches can force companies to place many of their operating systems on pause while they investigate the attack. This downtime can lead to a damaged reputation, loss of clients/customers, and, ultimately, less cash flow.
Reputation damage
Cyberattacks can also harm your business reputation. When a major data breach occurs, customers and clients may feel less secure with your company, causing them to pack up and leave. Additionally, when a company’s internal systems are down for an extended period, the stock price can drop. This is precisely what happened in the recent CrowdStrike IT outage.
A cybersecurity threat can lead to immediate financial burdens, such as fines and liability payments. However, reputation damage may be the hardest to overcome.
Legal liability
Another major consequence that can follow a cyberattack is legal penalties and fines. If your company fails to maintain proper cybersecurity measures and that lack of measures eventually leads to a cyberattack or data breach, you could be fined. Your company must be vigilant in cybersecurity prevention and follow specific processes for reporting incidents to avoid penalties.
For example, in 2024, Intercontinental Exchange was fined $10 million for violating data breach reporting rules.
Business continuity problems
Mapping out a business continuity plan (BC) is one of the most important steps a business can take to survive a cyberattack. This allows the company to continue with foundational functions during emergencies, such as power outages, data breaches, and cyberattacks. BCs have become increasingly important in recent years with the digitalization of practically everything in the business world. A business continuity plan can be the difference between a company failing or succeeding after a major cyber threat.
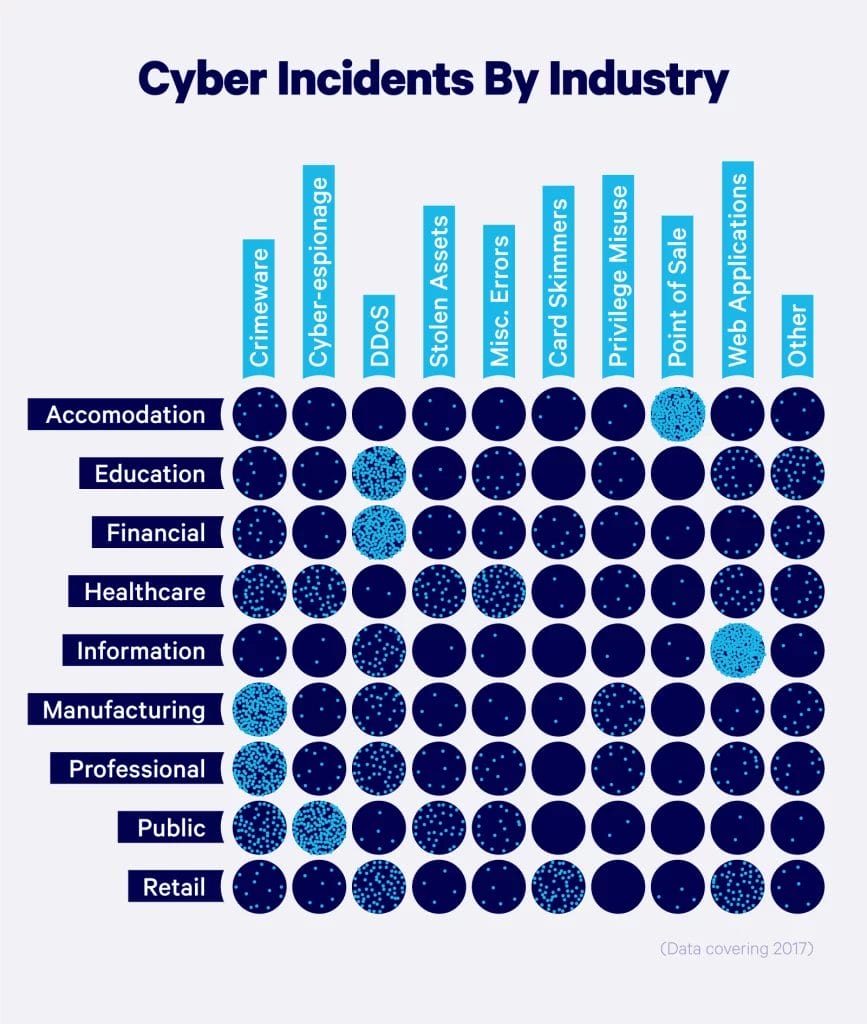
Cyberattacks by industry
Some industries are more vulnerable to cyberattacks than others, simply due to the nature of their business. Any industry can be affected by a data breach. However, businesses closely tied to people’s daily lives are at the highest risk.
Companies that hold sensitive data or personally identifiable information are common targets for hackers. Types of businesses or organizations that are most vulnerable to cyberattacks include:
Manufacturing
According to IBM’s 2024 Threat Intelligence Index, the manufacturing industry takes the cake with the largest number of cyberattacks in 2023. The cyber threat to the manufacturing industry has grown rapidly since 2019. At that time, manufacturing only experienced about 8% of all cyberattacks, while in 2023, it accounted for more than 25%! Manufacturers in the Asia Pacific region are particularly affected by cyber threats.
Banks and financial institutions
Unsurprisingly, the banking and finance sector was one of the most affected industries in 2023. Banking institutions hold lots of sensitive data such as credit card information, bank accounts, and personal customer or client data, so there is a major risk of losses in this industry.
Interestingly, the share of cyberattacks directed at the banking and financial industry has shrunk slightly from 23% in 2020 to 18.2% in 2023.
Professional services
The third most affected industry over the past couple of years was the professional and business services industry, which accounted for around 15% of all cyberattacks. This included accountancy and law firms, marketing agencies, IT, and others. These professionals hold sensitive data on clients, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
Energy
The energy sector accounted for 11% of all cyber incidents in 2023. This percentage has nearly doubled since 2019 and has been on a steady increase. Data breaches, hacking, and extortion are the biggest threats to the energy sector, causing major disruptions in the oil, gas, electric, and renewable energy sectors.
Supply chain
Cyber incidents affecting the supply chain have become increasingly common in recent years. Supply chain attacks have become more and more costly for businesses. By 2031, Cyber Ventures estimates that the global cost of supply chain attacks will cost businesses $130 billion. Between 2021 and 2023, supply chain attacks have increased by an alarming 431%, with projections indicating a continued rise through 2025
In the visual below, we break down common types of cyber incidents and their varying impacts on industries.
Cybersecurity industry statistics
As you might expect, the recent rise in cyber threats has increased the demand for cybersecurity. So, what is the current state of the cybersecurity industry?
Cybersecurity workforce at an all-time high
In 2023, there were an estimated 5.5 million workers in the cybersecurity industry, a 9% increase from 2022 and a number that has steadily grown over the past few years.
Cyber workforce expected to grow by 32%
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the American cybersecurity workforce will grow by 32% by 2032 and add around 53,000 new jobs. This is a significantly faster growth rate than other industries.
Cybersecurity job vacancies grew by 350%
While the tech industry was experiencing some massive layoffs, cybersecurity was growing. In the U.S. alone, there are currently 750,000 unfilled positions in the cybersecurity sector and a global shortage of more than 4 million!
Cyber liability insurance has grown exponentially in recent years as more businesses invest in policies to protect themselves from the growing risk of a cyberattack. That said, with the increased risk comes higher premiums. Cyber policy premiums rose by 11% in the first quarter of 2023 and 28% in the final quarter of 2022; many experts expect the number of incidents to continue to rise.
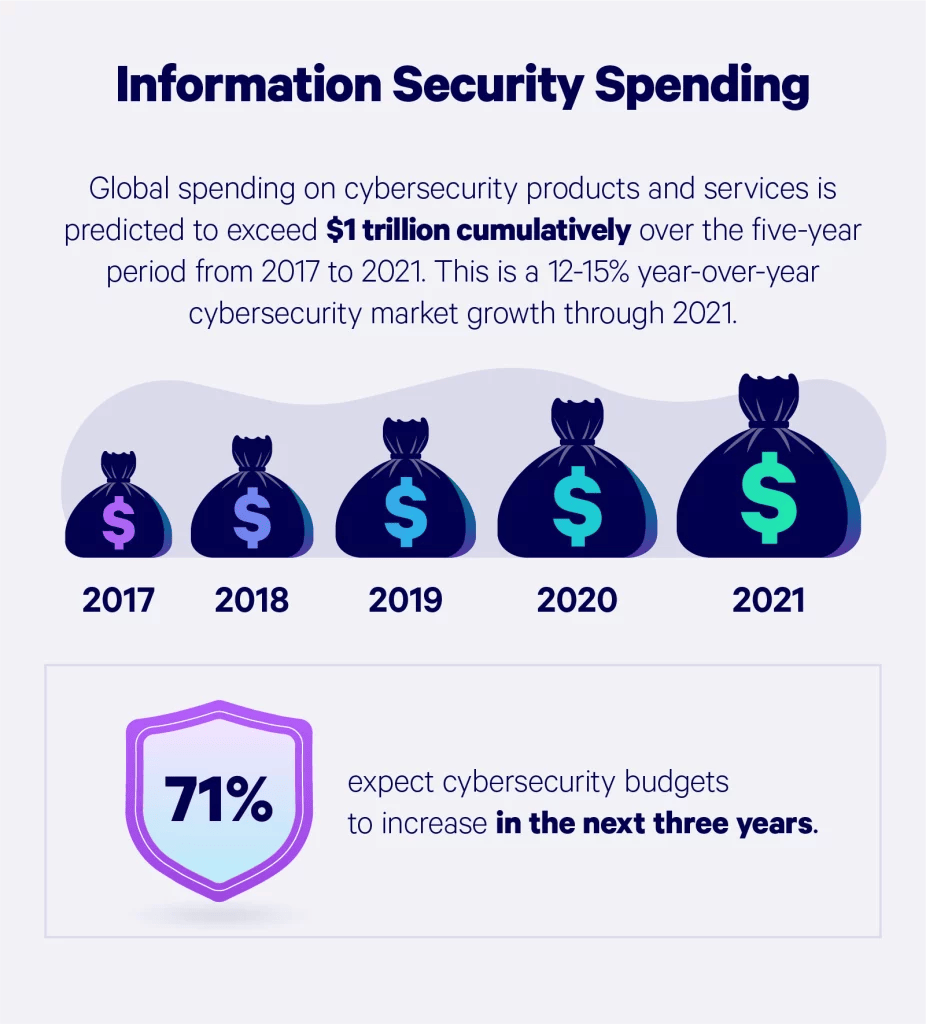
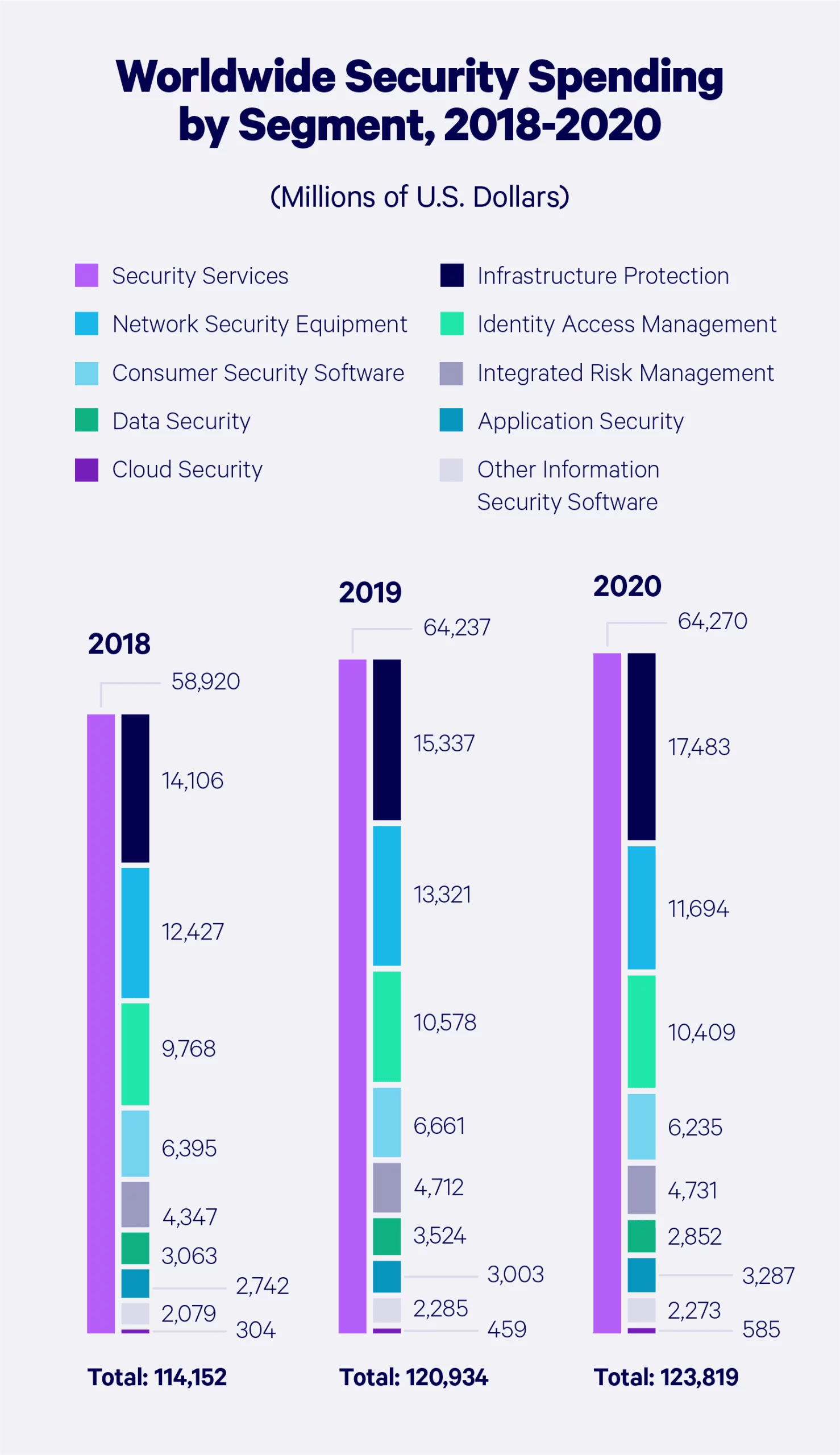
Information security spending
Statista Market Report’s information security spending reached $176 billion in 2023 and continued to rise through 2024. By 2030, this spending will likely be more than $300 billion, triple the amount spent in 2017.
Global security spending
Let’s take a look at how cybersecurity spending has grown around the globe — broken down by product or service.
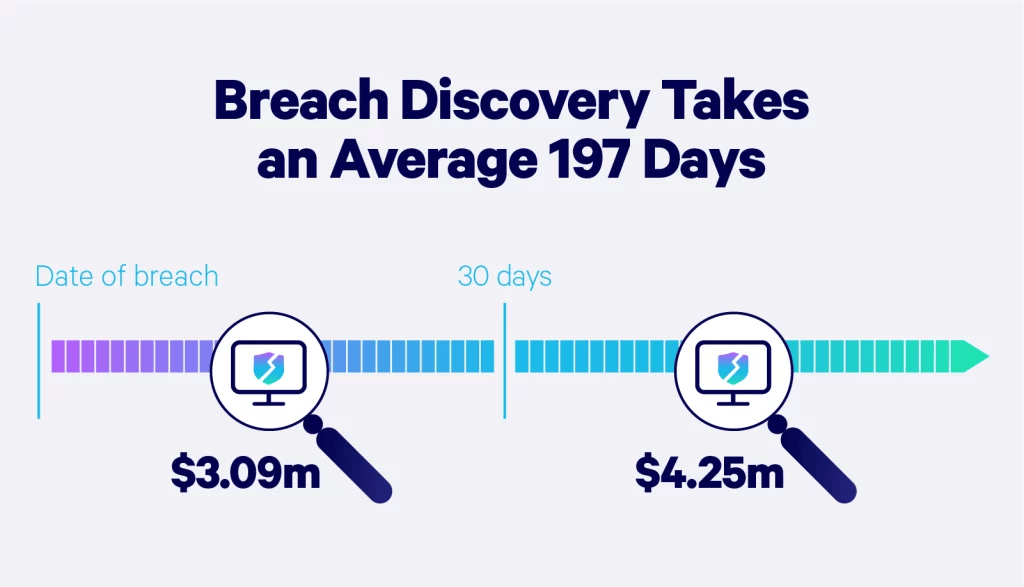
Data breach discovery statistics
“Breach discovery” refers to the point in time when the company or business becomes aware that an incident has occurred. According to IBM, it takes a company 204 days on average to discover the breach — and up to 73 days to contain it.
Additionally, AI-use in security systems significantly reduced the financial impact of cyberattacks. Companies that used extensive AI features discovered and contained data breaches 108 days sooner than those that didn’t. Data breaches also cost these companies $1.76 million less on average.
Companies that discovered and contained a data breach in fewer than 200 days saved more than $1 million compared to those that took more than 200 days. A slow response to a data breach can cause even more trouble for your company. It can result in a loss of customer trust, productivity, or significant fines.
A data breach response plan is a proactive way to prepare for a breach. Having a risk management strategy to combat incidents such as breaches can minimize their impact on your company and bottom line. An incident response plan, for example, guides your team through the phases of detection, containment, investigation, remediation, and recovery.
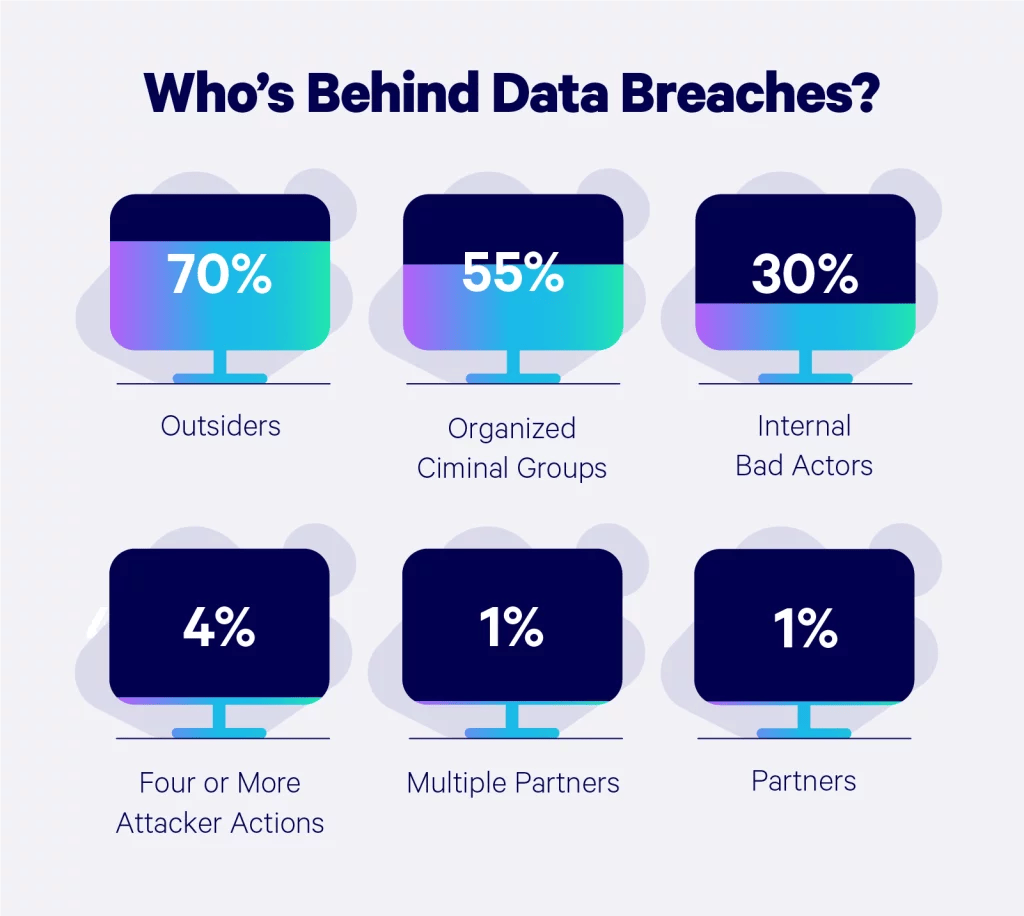
Who’s behind data breaches?
The average person might assume the files on a company database are a bunch of boring documents, but hackers know the hard truth about that hard drive.
According to Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report, the majority of cyberattacks are triggered by outsiders, insiders, company partners, organized crime groups, and affiliated groups. We break down the percentages of each:
- 65% external (organized crime, state-sponsored)
- 35% internal (employees, partners, etc.)
How to reduce the risk of cyberattacks
With the increasing threats of hackers mishandling your data, implementing processes to prevent data security breaches is the most responsible course of action after having adequate professional data breach insurance.
Data breach laws vary by state, so there are different factors to consider based on your company’s location.
Cyber threats are constantly evolving. Businesses that understand their Risk Profile are better prepared to defend against attacks. Assessing potential vulnerabilities can help you take targeted steps to improve security and minimize exposure. Find out where your business stands and how to stay protected. Get your Risk Profile.
1. Reduce data transfers
Transferring data between business and personal devices is often inevitable as a result of the increasing number of employees who work remotely. Keeping sensitive data on personal devices significantly increases vulnerability to cyberattacks.
2. Download carefully
Downloading files from unverified sources can expose your systems and devices to security risks. It’s important to only download files from sources and avoid unnecessary downloads to lower your device’s susceptibility to malware.
3. Improve password security
Password strength is the first line of defense against a variety of attacks. Using strings of symbols that don’t have a meaning, making regular password changes, and never writing them down or sharing them is crucial to protecting sensitive data.
4. Update device software
Software providers work hard to continuously make their software more secure and regularly installing the latest updates will make your devices less vulnerable to attacks.
5. Monitor for data leaks
Regularly monitoring your data and identifying existing leaks will help mitigate the potential fallout from long-term data leakage. Data breach monitoring tools actively monitor and alert you of suspicious activity.
6. Develop a breach response plan
Data breaches can happen to even the most careful and disciplined companies. Establishing a formal plan to manage potential data breach incidents, a primary cyber response plan, and a cybercrime recovery plan will help organizations of any size respond to actual attacks and contain their potential damage.
It’s clear that businesses are under a constant threat of cybercrime and must take steps to defend their data. Don’t wait until it’s too late! Take steps today to prevent future data breaches and the consequences that follow. Akin to the need for adequate cyber liability insurance, adequate data protection is essential.
Cyber security trends and predictions for 2025
As we navigate through 2025, the cybersecurity landscape continues to evolve, presenting both challenges and opportunities. Let’s take a look at what to expect in the future with data breaches and attacks.
Technological advances will automate many historically manual processes
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into cybersecurity is automating tasks traditionally performed by humans. This improves efficiency, accuracy, and response times when dealing with cyber risk management.
AI-driven attacks will become more common
Artificial intelligence has taken the world by storm and has now become prevalent in almost every industry. AI tools are used by both cybercriminals and the IT professionals working to prevent attacks. An estimated 40% of all cyber incident are now AI-driven, and the best way to respond to such attacks is to incorporate AI tools into your risk management plan.
Data governance laws will continue to evolve
The regulatory landscape for information sharing, and data handling and processing is always changing. Data governance rules can differ depending on the location of your business and client base. Companies should expect the regulatory guidelines for cyber security and data handling to continue to change in 2025 and beyond.
State-sponsored cyber incidents will be commonplace in modern warfare
Cyber warfare has rapidly evolved in recent years. Many major world leaders have invested in cybersecurity to fend off state-sponsored attacks and cyber terrorism. The Russia-Ukraine conflict is a recent example of nations weaponizing cyber threats. Russian cyber attacks targeted Ukraine’s infrastructure more than 4,315 times in 2024, which was a 70% increase from the previous year.